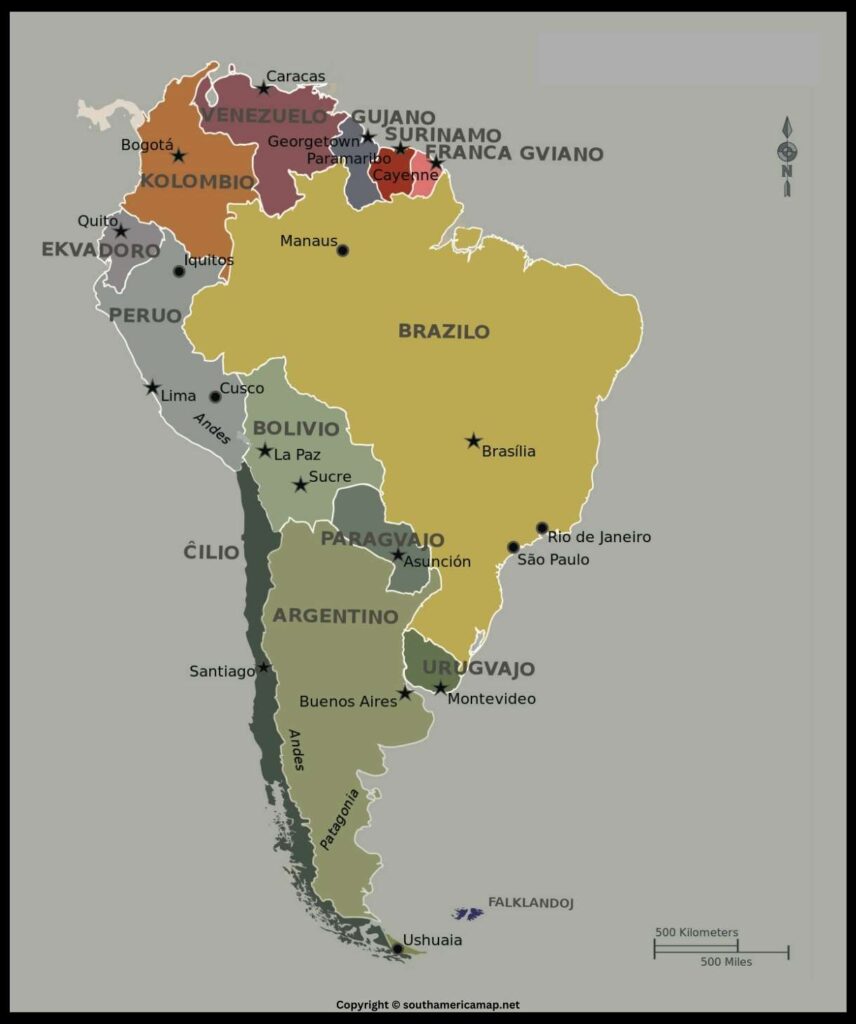
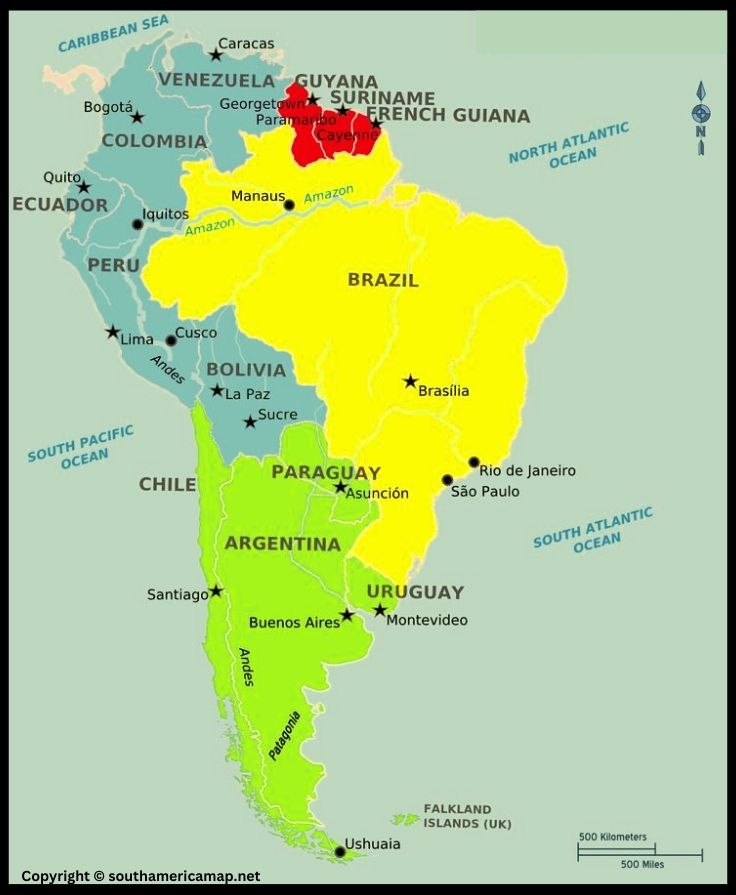
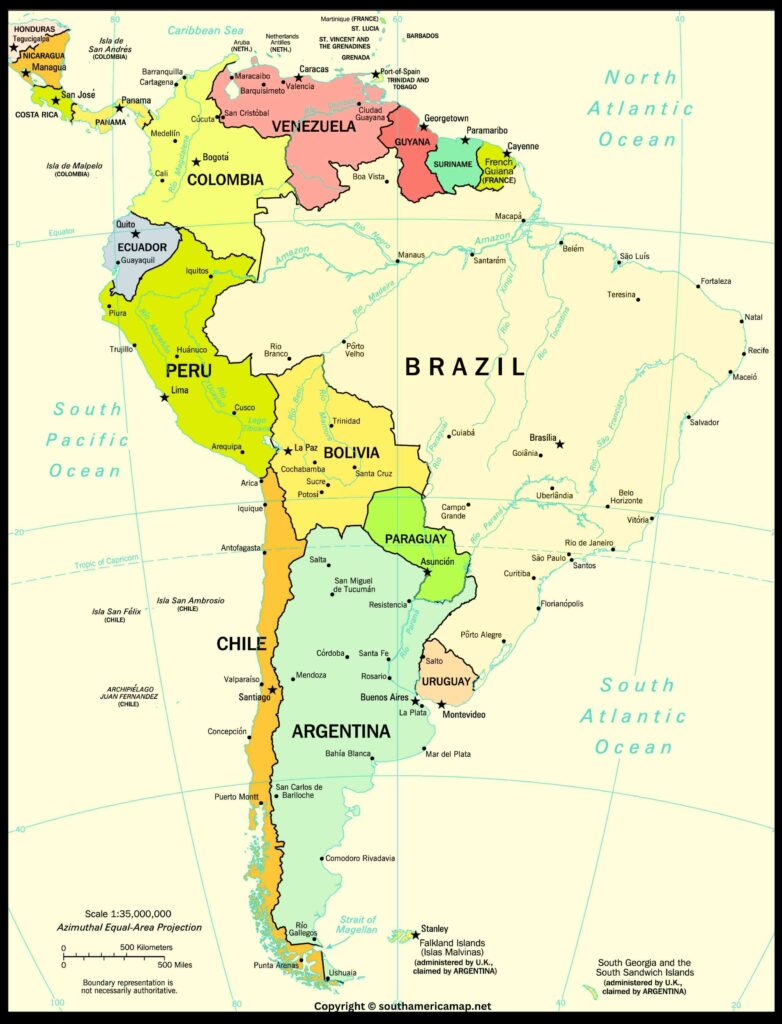
South America Map with Countries, Central & North America
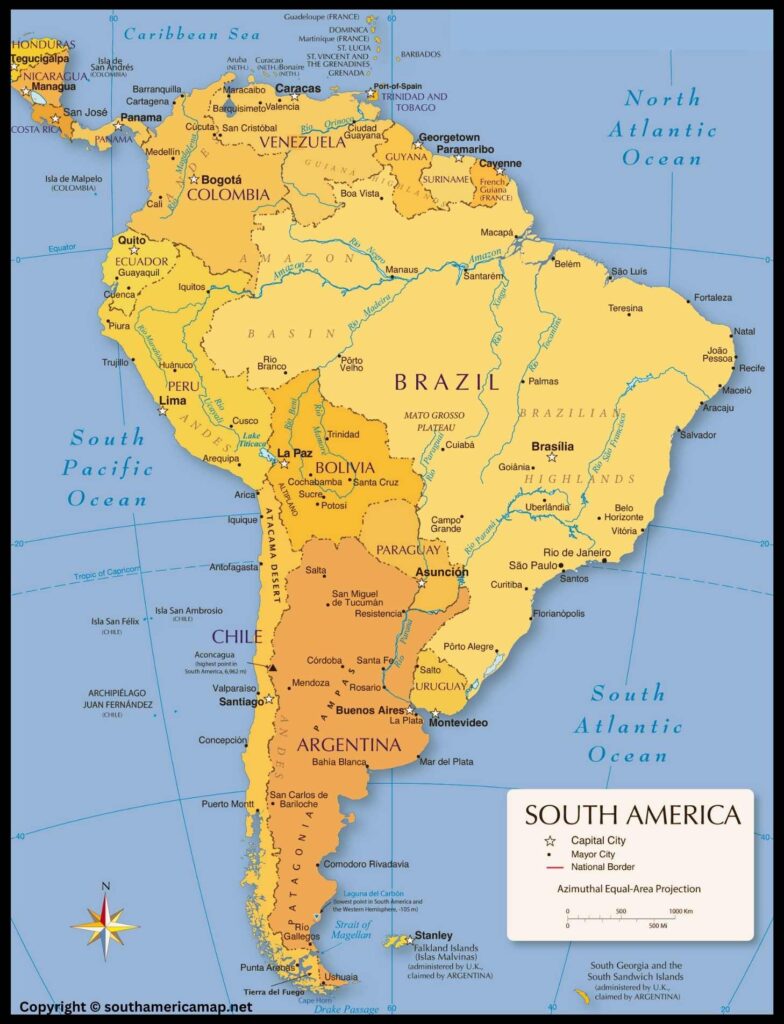
South America Map – South America sits as a triangular landmass, primarily located in the Western Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere. Its northernmost point, Punta Gallinas in Colombia, breaches into the Northern Hemisphere by a small margin.
Borders:
✔ West: The vast expanse of the Pacific Ocean shapes South America’s western coast, stretching from Colombia in the north to Chile in the south.
✔ North: The Caribbean Sea borders the northwest, separating South America from Central America and the Caribbean islands. Further north, the Atlantic Ocean takes over, forming the continent’s northern boundary.
✔ East: The mighty Atlantic Ocean continues to define South America’s eastern edge, stretching all the way down to the southern tip.
✔ South: The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, engulfs the southernmost point of South America, Cape Horn in Chile.
Landmass:
South America is the fourth-largest continent, boasting a diverse range of landscapes within its roughly 18 million square kilometers. Its landmass can be broadly divided into several distinct regions:
✔ Andean Mountains: The mighty Andes Mountains form the backbone of South America, stretching along the western coast from Tierra del Fuego in the south to Colombia in the north. These towering peaks and volcanic ranges act as a natural barrier, dramatically influencing the continent’s climate, flora, and fauna.
✔ Amazon Basin: The sprawling Amazon Basin, located primarily in Brazil, is the largest rainforest on Earth. This verdant region, dubbed the “lungs of the planet,” is home to an unparalleled biodiversity and plays a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns.
✔ Patagonia: In the southernmost tip of South America lies Patagonia, a windswept region characterized by steppes, glaciers, and rugged mountains. This sparsely populated region offers breathtaking natural beauty and a glimpse into the continent’s ancient past.
✔ Guiana Highlands: The Guiana Highlands encompass a vast area of ancient crystalline rocks in northern South America, encompassing portions of Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and Brazil. This region is home to diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, and tepuis (flat-topped mountains).
✔ Eastern Lowlands: The Eastern Lowlands occupy the eastern and northeastern portions of South America, stretching from the Atlantic coast to the foothills of the Andes. This fertile region is home to expansive plains and rolling hills, supporting a variety of agricultural activities and diverse ecosystems.
Island Territories:
South America includes numerous islands, some of which are geographically and culturally distinct. These include the Galapagos Islands, renowned for their unique wildlife, and the Falkland Islands, which have been the subject of historical territorial disputes.
South America Map
Map of South America serves a multitude of purposes, playing a vital role in various aspects of our lives. Here are some key reasons why South America maps are important and how they are used:
Navigation and Travel:
Physical maps: These maps provide detailed information about the continent’s physical features, including mountains, rivers, lakes, deserts, and forests. They assist travelers in planning routes, navigating unfamiliar terrain, and appreciating the diverse landscapes of South America.
Political maps: These maps depict the continent’s political boundaries, including countries, states, provinces, and major cities. They are essential for understanding political geography, planning travel routes between different countries, and navigating within specific regions.
Education and Research:
- Learning about geography: Maps are crucial tools for students and educators to learn about South America’s geography. They help visualize the continent’s size, shape, location, and diverse landscapes.
- Conducting research: Researchers from various disciplines, including anthropology, ecology, geology, and history, rely on maps to analyze spatial patterns, track changes, and conduct field research across the continent.
Resource Management and Planning:
- Natural resources exploration: Maps provide valuable information about the distribution of natural resources, such as minerals, oil, and timber. This information assists governments and businesses in planning resource exploration and extraction activities.
- Environmental protection: Maps are essential for monitoring environmental changes, identifying vulnerable ecosystems, and managing protected areas. They aid in planning sustainable development strategies and implementing conservation efforts.
- Infrastructure development: Maps are crucial for planning and constructing infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, power lines, and communication networks. They ensure efficient transportation, communication, and energy distribution across the continent.
Business and Commerce:
- Market analysis: Businesses use maps to identify potential markets, analyze competitor locations, and plan distribution networks. This information is crucial for business development and expansion within South America.
- Logistics and transportation: Maps are vital for planning efficient transportation routes for goods and services across the continent. This ensures timely delivery and reduces logistical costs.
- Tourism industry: Maps are essential tools for promoting tourism in South America. They help tourists plan their travel itineraries, identify attractions, and navigate destinations.
Cultural Understanding:
- Exploring cultural diversity: Maps can be used to learn about the different cultures and ethnicities that exist in South America. This promotes understanding and appreciation for the continent’s rich cultural heritage.
- Understanding history: Historical maps provide valuable insights into the evolution of political boundaries, population distribution, and trade routes over time. This knowledge helps us understand the present by learning from the past.
Map of Central And South America
Central America:
- Geography: A narrow landmass bridging North America and South America, bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Comprised of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama.
- Landscape: Dominated by mountains, volcanoes, rainforests, and coastlines. The highest peak is Tajumulco in Guatemala. Active volcanoes, including Fuego and Arenal, pose a constant threat.
- Climate: Tropical throughout, with distinct wet and dry seasons. Coastal regions are hot and humid, while highlands experience cooler temperatures.
- Biodiversity: A hotspot for biodiversity, boasting numerous rainforests, mangroves, and coral reefs. Supports a wide variety of plants and animals, including jaguars, monkeys, sloths, and colorful birds.
- Culture: Rich cultural heritage shaped by indigenous peoples, Spanish colonization, and African influence. Diverse languages, traditions, and cuisine vary across the region.
South America:
- Geography: The fourth-largest continent, encompassing diverse landscapes ranging from snow-capped Andes Mountains to the vast Amazon rainforest. Bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Caribbean Sea to the north.
- Landscape: Diverse, including towering mountain ranges, expansive plains, lush rainforests, arid deserts, and long coastlines. The iconic Andes Mountains form the backbone, while the Amazon Basin covers a significant portion of the north.
- Climate: Varies greatly depending on location, with tropical climates in the north and colder temperatures in the south. Andean highlands experience high altitudes and glacial peaks, while Patagonian plains boast arid conditions.
- Biodiversity: A treasure trove of biodiversity, home to the largest rainforest and diverse ecosystems ranging from glaciers to coral reefs. Supports an abundance of unique flora and fauna, including jaguars, pumas, monkeys, sloths, anacondas, and exotic birds.
- Culture: Rich and vibrant, influenced by indigenous traditions, Spanish colonization, and African heritage. Diverse languages, music, dance, and cuisine vary across the continent.
Connections:
- Geographical Link: Central America acts as a bridge between North and South America, with cultural and ecological connections to both continents.
- Shared History: Both regions share a history of Spanish colonization, shaping their cultural and linguistic landscapes.
- Biodiversity Corridor: Central and South America form a vital corridor for wildlife migration, supporting the movement of various species across the continents.
- Economic Partnership: Trade and economic ties bind the regions together, promoting development and cooperation.
Uniqueness:
- Central America: Known for its active volcanoes, Mayan ruins, vibrant coral reefs, and lush rainforests.
- South America: Home to the Amazon rainforest, the Andes Mountains, the iconic Galapagos Islands, and diverse cultural traditions.
Both Central and South America offer a kaleidoscope of vibrant cultures, breathtaking landscapes, and unique experiences, captivating the hearts of explorers and travelers alike.
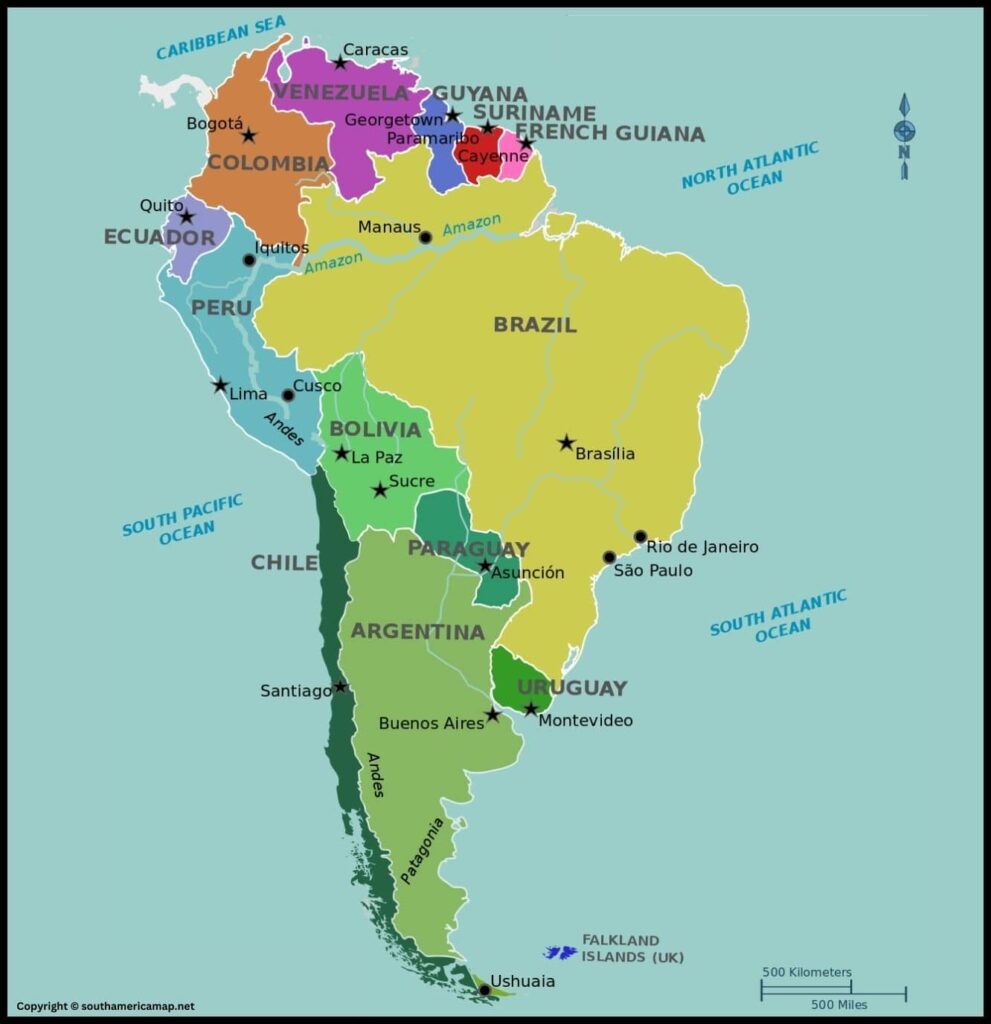
Map of North And South America
The map of North and South America depicts the two continents in the Western Hemisphere, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
North America:
- Countries: The major countries in North America include the United States, Canada, Mexico, and several smaller countries in Central America.
- Geographical Features: Notable geographical features include the Rocky Mountains in the western part of North America, the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern part, the Great Plains, the Mississippi River, and the Great Lakes.
- Cities: Major cities such as New York, Los Angeles, Toronto, and Mexico City are prominently marked.
Central America:
- Countries: Central American countries, including but not limited to Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
- Geographical Features: The region is characterized by volcanic activity, dense tropical rainforests, and a series of mountain ranges.
South America:
- Countries: Major countries in South America include Brazil, Argentina, Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Chile, and many others.
- Geographical Features: The Andes mountain range runs along the western edge of South America, making it the longest mountain range in the world. The Amazon Rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest on Earth, is a prominent feature in the northern part of the continent.
- Rivers: The Amazon River, the second-longest river globally, flows through the heart of the rainforest. Other significant rivers include the Paraná, Orinoco, and the Uruguay River.
Islands and Archipelagos:
- Caribbean Islands: Numerous islands dot the Caribbean Sea, including the Greater Antilles (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico) and the Lesser Antilles (a chain of smaller islands).
- Galápagos Islands: Off the western coast of South America, these islands are famous for their unique wildlife and played a crucial role in Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution.
Oceans and Seas:
- Atlantic and Pacific Oceans: These oceans border the eastern and western coasts of the Americas, respectively.
- Caribbean Sea: Situated to the southeast of the Gulf of Mexico, it is surrounded by the Caribbean islands.
- Political Boundaries: International borders between countries are clearly marked, helping to identify the distinct nations across the continents.
South America Map Countries
| Country | Capital |
| Argentina | Buenos Aires |
| Bolivia | Sucre (official), La Paz (administrative) |
| Brazil | Brasília |
| Chile | Santiago |
| Colombia | Bogotá |
| Ecuador | Quito |
| Guyana | Georgetown |
| Paraguay | Asunción |
| Peru | Lima |
| Suriname | Paramaribo |
| Uruguay | Montevideo |
| Venezuela | Caracas |
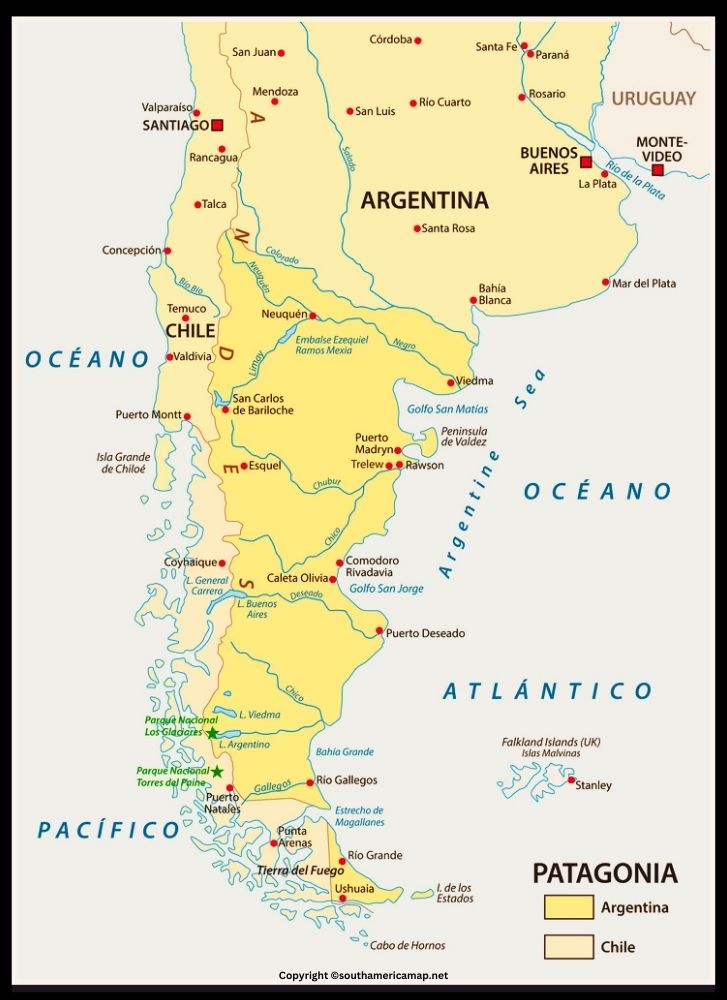
Map of Patagonia South America
Patagonia, the wild and rugged land at the southernmost tip of South America, offers a breathtaking tapestry of diverse landscapes. Let’s explore its map and discover its secrets.
- West: Bordered by the Pacific Ocean, offering stunning coastlines with fjords, cliffs, and rugged islands.
- North: Defined by the Colorado River, except for a small Andean portion extending north.
- East: Bathed by the Atlantic Ocean, featuring sandy beaches, rocky shores, and the Valdés Peninsula known for its marine life.
- South: The Strait of Magellan separates it from Tierra del Fuego, an island also often considered part of Patagonia.
Landmarks and Regions:
- Andes Mountains: The backbone of Patagonia, stretching north to south with snow-capped peaks, glaciers, and volcanoes like Fitz Roy and Cerro Torre.
- Torres del Paine National Park: Located in Chile, this UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve boasts granite peaks, turquoise lakes, and glaciers like Grey Glacier.
- Perito Moreno Glacier: A massive glacier in Argentina, advancing into the waters of Lake Argentino and calving spectacular icebergs.
- Patagonian Steppes: A vast, arid region with rolling hills, grasslands, and abundant wildlife like guanacos, rheas, and armadillos.
- Tierra del Fuego: A large island shared by Argentina and Chile, known for its windswept landscapes, penguin colonies, and Ushuaia, the southernmost city in the world.
Map of North And South America
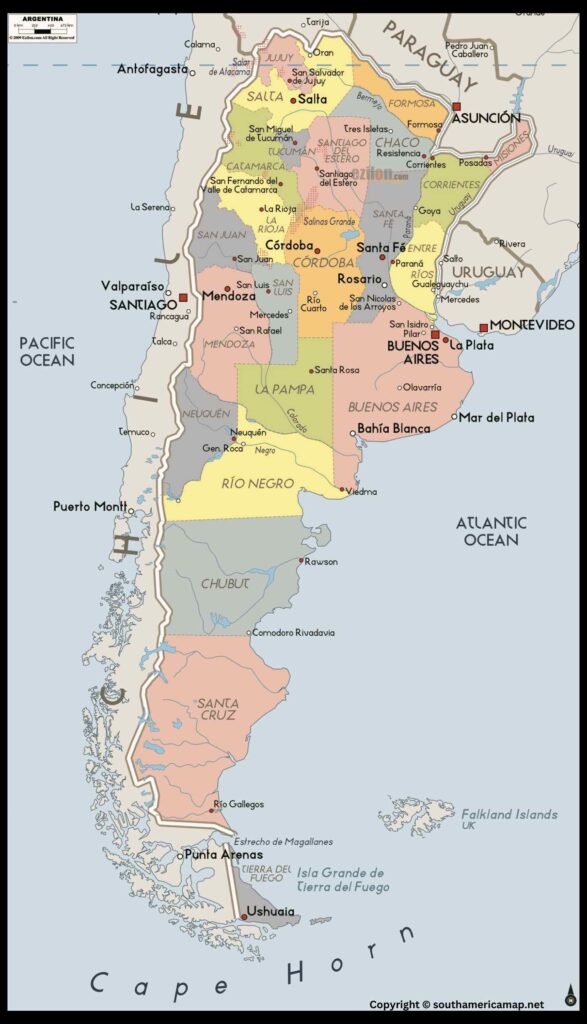
Argentina, the second-largest country in South America, is a land of captivating contrasts and breathtaking beauty. From the snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the expansive plains of the Pampas, the Iguazu Falls to the vibrant tango halls of Buenos Aires, Argentina offers something for everyone
Geography:
- Location: Situated in the southernmost part of South America, Argentina shares borders with Chile, Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil, Uruguay, and the Drake Passage.
- Landmarks: The iconic Andes Mountains form the western border with Chile, while the vast Pampas grasslands dominate the central region. The Iguazu Falls, one of the world’s most spectacular waterfalls, straddle the border with Brazil.
- Climate: Argentina experiences a wide range of climates, from the subarctic conditions in the south to the subtropical heat in the north.
Culture:
- Indigenous heritage: Argentina’s diverse indigenous cultures have left their mark on the country’s history, art, and cuisine.
- Spanish influence: The arrival of Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century had a profound impact on Argentina, shaping its language, religion, and architecture.
- European immigration: Waves of immigrants from Europe, particularly Italy and Spain, contributed to Argentina’s unique cultural identity.
- Arts and music: Argentina is renowned for its vibrant arts scene, including tango dance, literature, and theater.
Attractions:
- Buenos Aires: The vibrant capital city offers a captivating blend of European elegance and Latin American flair. Explore historic neighborhoods like San Telmo and La Boca, marvel at the Teatro Colón opera house, and catch a passionate tango performance.
- Iguazu Falls: Witness the awe-inspiring spectacle of the Iguazu Falls, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Hike through the lush rainforest, feel the spray of the cascading water, and experience the power of nature.
- Bariloche: Nestled in the foothills of the Andes, Bariloche is a popular destination for outdoor enthusiasts and nature lovers. Enjoy skiing, hiking, kayaking, and breathtaking views of the surrounding mountains and lakes.
- Patagonia: This vast region at the tip of South America offers a wilderness paradise with glaciers, mountains, fjords, and diverse wildlife. Trek through Torres del Paine National Park, sail on glaciers, or spot penguins and whales.
Food and Wine:
Argentina is known for its delicious cuisine, influenced by its diverse cultural heritage. Sample a juicy steak on the grill, indulge in fresh seafood, or try the local empanadas. Don’t forget to pair your meal with a glass of Argentinian Malbec wine, one of the country’s most famous exports.
Festivals:
Argentina’s vibrant culture is reflected in its numerous festivals throughout the year. Immerse yourself in the Carnival celebrations in February, experience the passion of the Buenos Aires Tango Festival in July, or join the crowds at the gaucho festivals in the Pampas.
Map of North And South America
| Country | Capital |
| Argentina | Buenos Aires |
| Bolivia | Sucre (official), La Paz (administrative) |
| Brazil | Brasília |
| Chile | Santiago |
| Colombia | Bogotá |
| Ecuador | Quito |
| Guyana | Georgetown |
| Paraguay | Asunción |
| Peru | Lima |
| Suriname | Paramaribo |
| Uruguay | Montevideo |
| Venezuela | Caracas |
Overall, South America map are indispensable tools for navigating, educating, researching, managing resources, conducting business, and exploring the continent’s diverse cultures. They offer a unique and powerful lens through which we can understand, appreciate, and interact with this fascinating region of the world.